Contents
Ch01: Spatial Reference Systems (SRS)
- Spatial Reference Systems - coordinate system to identify particular points on the earth (e.g. WGS84)
- geoid - the word used to describe the shape of the earth.
- reference ellipsoid - a smooth model used by scientists to approximate the shape of the earth.
- oblate spheroid - most commonly used reference ellipsoid
- Most reference ellipsoids aren't meant to model the entire earth, but some such as the World Geodetic System 1984 do.
- SQL Server 2012 recognizes spatial reference systems based on a number of different reference ellipsoids.
Ellipsoid Name |
Semi-Major Axis (m) |
Semi-Minor Axis (m) |
Inverse Flattening |
Area of Use |
Airy (1830) |
6,377,563.396 |
6,356,256.909 |
299.3249646 |
Great Britain |
Bessel (1841) |
6,377,397.155 |
6,356,078.963 |
299.1528128 |
Czechoslovakia, Japan, South Korea |
Clarke (1880) |
6,378,249.145 |
6,356,514.87 |
293.465 |
Africa |
NAD 27 |
6,378,206.4 |
6,356,583.8 |
294.9786982 |
North America |
NAD 83 |
6,378,137 |
6,356,752.3 |
298.2570249 |
North America |
WGS 84 |
6,378,137 |
6,356,752.314 |
298.2572236 |
Global |
The above table demonstrates the Size/Shape characteristics of a SRS.
To complete the package we need reference points to place the ellipsoid in the correct position relative to the earth.
Definition [Spatial Reference System] A geodetic datum is made up of a reference ellipsoid and a set of reference points to position the ellipsoid relative to the earth.
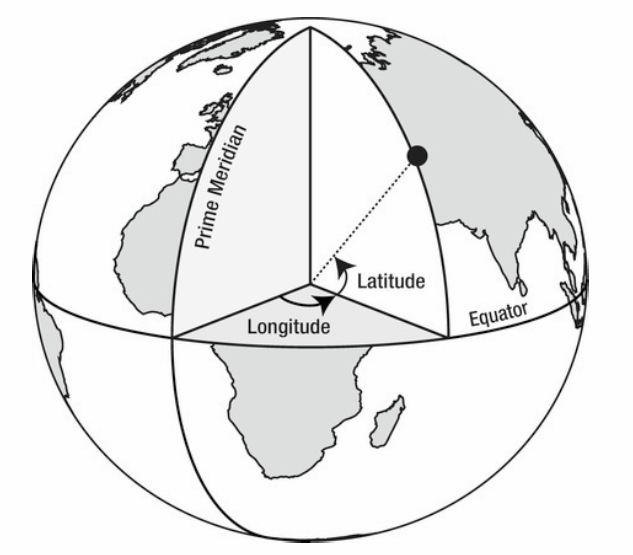
Geographic Coordinate Systems
- Latitude - 0 degrees at equator, 90 degrees at the north pole, -90 degrees at the south pole.
- Longitude - 0-180 degrees east or west of the prime meridian
Projected Coordinate Systems
Because we carry maps on flat surfaces (instead of geoids), the area of the world that we want to see on the map needs to be projected onto the Cartesian coordinate plane.
- Conformal Projection - any projection that preserves the local shape of objects on the resulting map.
Mercador projection is such a map projection and is used by Bing and Google maps.
Universal Transverse Mercator Projection is a grid composed of many projections laid side by side. Globe is sliced (north/south) into 60 strips (of 6 degrees each). Each strip is divided at the equator. E.g. Chattanooga, TN is in Zone 16N.
Projection Parameters
Azimuth |
The angle at which the center line of the projection lies, relative to north (measured clockwise from north) |
Central meridian |
The line of longitude used as the origin from which x coordinates are measured |
False easting |
A value added to x coordinates so that stated coordinate values remain positive over the extent of the map |
False northing |
A value added to y coordinates so that stated coordinate values remain positive over the extent of the map |
Latitude of center |
The latitude of the point at the center of the map projection |
Latitude of origin |
The latitude used as the origin from which y coordinates are measured |
Latitude of point |
The latitude of a specific point on which the map projection is based |
Longitude of center |
The longitude of the point at the center of the map projection |
Longitude of point |
The longitude of a specific point on which the map projection is based |
Scale factor |
A scaling factor used to reduce the effect of distortion in a map projection |
Standard parallel |
A line of latitude along which features on the map have no distortion |
- Easting - X Coordinate (measured east of origin)
- Northing - Y Coordinate (measured north of origin)
Components of a Spatial Reference System
Component |
Function |
Coordinate system |
Specifies a mathematical framework for determining the position of items relative to an origin. Coordinate systems used in SQL Server are generally either based on geographic or projected coordinate systems. |
Datum |
States a model of the earth onto which we can apply the coordinate system. Consists of a reference ellipsoid (a three-dimensional mathematical shape that approximates the shape of the earth) and a reference frame (a set of points to position the reference ellipsoid relative to known locations on the earth). |
Prime meridian |
Defines the axis from which coordinates of longitude are measured. |
Projection (a) |
Details the parameters required to create a two-dimensional image of the earth’s surface (i.e., a map), so that positions can be defined using projected coordinates. Unit of measurement Provides the appropriate unit in which coordinate values are expressed. |
(a) Projection parameters are only defined for spatial reference systems based on projected coordinate systems.
Spaitial Reference Identifiers (SRIDs)
SRIDs identify all the data like a pointer. E.g. 4326 = WGS84; 32136 = Tennessee State Plane. See details at http://www.epsg-registry.org/.
Well-Known Text (WKT) format is an industry standard format for expressing spatial information defined by the Open Geospatial Consortium (OGC).
Try the following:
SELECT well_known_text FROM sys.spatial_reference_systems WHERE authority_name = 'EPSG' AND authorized_spatial_reference_id = 4326;
Results in:
GEOGCS["WGS 84", DATUM["World Geodetic System 1984", ELLIPSOID["WGS 84", 6378137, 298.257223563]], PRIMEM["Greenwich", 0], UNIT["Degree", 0.0174532925199433]]
GEOGCS | PROJCS |
Geographic or projected coordinate system |
"WGS 84" |
Name of the SRS |
DATUM |
[Name, ELLIPSOID, PRIMEM, UNIT] |
ELLIPSOID |
Name, Semimajor axis of 6,378,137 meters, inverse flattening ration of 298.257223563 |
PRIMEM |
longitudinal line through Greenwich is the 0 or prime meridian |
UNIT |
measured in degrees. To convert from radians $$d=0.0174532925199433 \cdot r$$ (or just to $$d = \frac{pi}{180} \cdot r$$ ) |
Another example for projected is the Tennessee state plane:
PROJCS["NAD83 / Tennessee",
GEOGCS["NAD83",
DATUM["North_American_Datum_1983",
SPHEROID["GRS 1980",6378137,298.257222101,
AUTHORITY["EPSG","7019"]],
AUTHORITY["EPSG","6269"]],
PRIMEM["Greenwich",0,
AUTHORITY["EPSG","8901"]],
UNIT["degree",0.01745329251994328,
AUTHORITY["EPSG","9122"]],
AUTHORITY["EPSG","4269"]],
UNIT["metre",1,
AUTHORITY["EPSG","9001"]],
PROJECTION["Lambert_Conformal_Conic_2SP"],
PARAMETER["standard_parallel_1",36.41666666666666],
PARAMETER["standard_parallel_2",35.25],
PARAMETER["latitude_of_origin",34.33333333333334],
PARAMETER["central_meridian",-86],
PARAMETER["false_easting",600000],
PARAMETER["false_northing",0],
AUTHORITY["EPSG","32136"],
AXIS["X",EAST],
AXIS["Y",NORTH]]■ Note The Well-Known Text format in which SQL Server stores the properties of spatial reference systems in the sys.spatial_reference_systems table is exactly the same format as used in the .PRJ file used to describe the spatial reference in which the data in an ESRI shapefile are stored.
David Mercer and Thomas Olsen presented this chapter. See "Still waiting for file"...