Virtual Network Configuration
Below is a diagram that shows how your virtual network sees the world and how the world sees it. We have eliminated for the moment the complications of the <<latex($\mu$)>>Cloud. The IP address 216.249.119.123 is a place holder for your IP address.
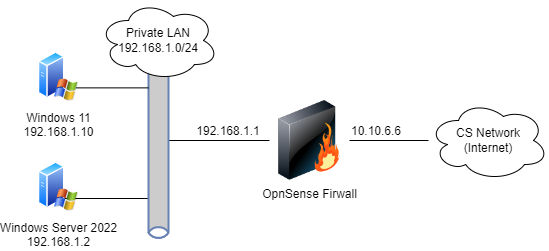
In order for you to do port forwarding for your server, you must setup the iptable rules. We need two pieces of functionality:
- NAT
Port forwarding 3389 -> 192.168.1.2:3389 and 3390 --> 192.168.1.3:3389
To setup NAT on Ubuntu, see Ubuntu NAT. We'll add a short bit of instructions to the system to forward the ports as follows:
#Port Forwarding Stuff: iptables -t nat -A PREROUTING -i eth0 -p tcp -d 216.249.119.[your ip] --sport 1024:65535 --dport 3389 -j DNAT --to-destination 192.168.1.2 iptables -t nat -A PREROUTING -i eth1 -p tcp -d 216.249.119.[your ip] --sport 1024:65535 --dport 3389 -j DNAT --to-destination 192.168.1.2 iptables -t nat -A PREROUTING -i eth0 -p tcp -d 216.249.119.[your ip] --sport 1024:65535 --dport 3390 -j DNAT --to-destination 192.168.1.3:3389 iptables -t nat -A PREROUTING -i eth1 -p tcp -d 216.249.119.[your ip] --sport 1024:65535 --dport 3390 -j DNAT --to-destination 192.168.1.3:3389
NOTE: ALL OF THIS CAN BE FOUND BY TYPE "man iptables" from the command line in linux.
Connecting to Samuel and dealing with Certificate Errors
- Download the certificate files listed below
On your windows machine, run mmc.exe as administrator. (this was our problem in class)
- File, Add/Remove Snap-ins
- Select Certificates and click ADD. Select Computer Account, and click finish.
- Click Ok.
- Expand Certificates and right click on Trusted Root Certificate Authority, Select All Tasks, Import
- Walk through the wizard importing the certificates you downloaded. (Make sure they are being put in the Trusted Root Certificate Authority folder).
